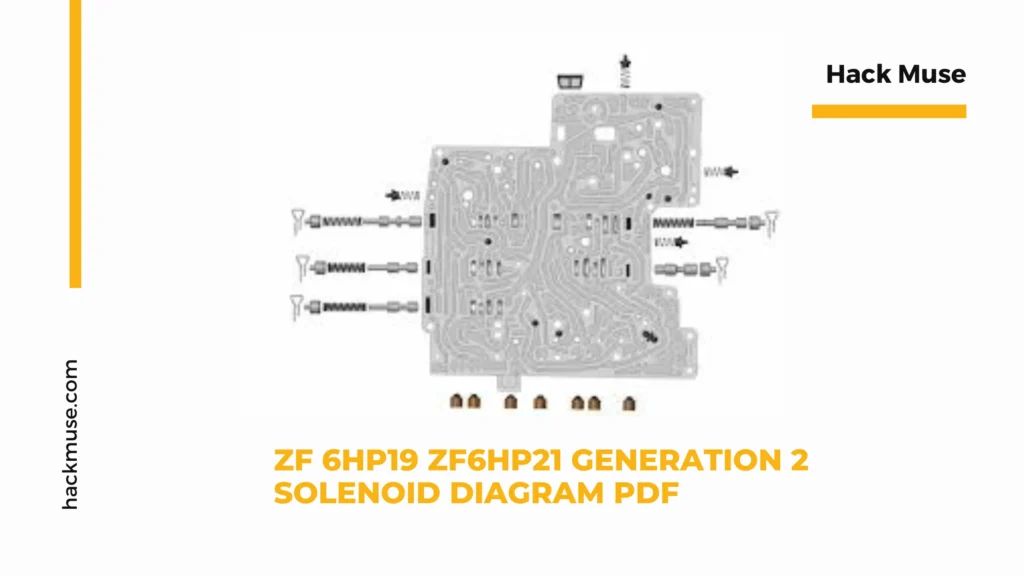
The ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 transmissions are renowned for their robustness and advanced technology. These second-generation automatic transmissions, used in a variety of vehicles, have become industry standards due to their reliability and performance. A crucial component of these transmissions is the solenoid pack, which controls the flow of transmission fluid and ensures smooth gear shifts. Understanding the solenoid diagram is essential for anyone involved in the maintenance or repair of these transmissions. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the ZF 6hp19 ZF6hp21 Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram PDF, addressing its importance, components, and common issues.
Introduction to ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 Transmissions
The ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 are six-speed automatic transmissions designed and manufactured by ZF Friedrichshafen AG. They are widely used in luxury and high-performance vehicles from brands such as BMW, Audi, and Jaguar. These transmissions are known for their high efficiency, smooth shifting, and durability.
The “HP” in the model name stands for “Hoch Präzision,” German for “high precision,” reflecting the meticulous engineering and quality control involved in their production. The “6” indicates the number of forward gears, while “19” and “21” refer to the transmission’s torque capacity.
Importance of the Solenoid in Automatic Transmissions
In automatic transmissions, solenoids play a critical role in controlling the hydraulic circuits that manage gear shifting. The solenoids are electrically controlled valves that regulate the flow of transmission fluid to different components within the transmission. This precise control ensures smooth and accurate gear changes, contributing to the overall performance and efficiency of the vehicle.
For the ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 transmissions, the solenoid pack consists of several solenoids that work together to manage the transmission’s operation. Each solenoid has a specific function, such as controlling the pressure for gear engagement or modulating the torque converter lock-up.
Overview of the ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram
The solenoid diagram for the ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 generation 2 transmissions provides a detailed illustration of the solenoid pack’s layout and connections. It is a crucial reference for technicians and mechanics when diagnosing issues, performing maintenance, or carrying out repairs.
The diagram typically includes:
- Solenoid Identification: Each solenoid is labeled with a unique identifier, making it easy to distinguish between them.
- Electrical Connections: The wiring connections to each solenoid are shown, including the power supply and control signals from the transmission control unit (TCU).
- Hydraulic Pathways: The diagram illustrates the hydraulic circuits that each solenoid controls, highlighting the flow of transmission fluid.
- Component Locations: The physical placement of each solenoid within the transmission is depicted, assisting in locating and accessing them during service procedures.
Common Issues with ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 Solenoids
Despite their reliability, the solenoids in the ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 transmissions can experience issues over time. Common problems include:
- Electrical Failures: Solenoids may fail due to electrical issues such as short circuits, open circuits, or faulty wiring. These problems can cause erratic shifting or prevent the transmission from engaging certain gears.
- Hydraulic Leaks: Wear and tear can lead to hydraulic leaks within the solenoid pack, resulting in insufficient fluid pressure and poor transmission performance.
- Contamination: Dirt, debris, or metal particles can contaminate the transmission fluid, clogging the solenoids and affecting their operation.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the solenoids can wear out due to the high pressures and temperatures they operate under, leading to diminished performance or failure.
Diagnosing and Repairing Solenoid Issues
Proper diagnosis and repair of solenoid issues in the ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 transmissions require a thorough understanding of the solenoid diagram and the transmission’s operation. Here are the general steps involved:
- Diagnostic Scanning: Use a diagnostic scanner to read fault codes from the TCU. These codes can provide valuable information about which solenoids are malfunctioning.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the solenoid pack for signs of damage, wear, or contamination. Check the wiring connections for any loose or damaged wires.
- Electrical Testing: Use a multimeter to test the electrical resistance of each solenoid. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications to identify any solenoids that are out of range.
- Hydraulic Testing: Check the transmission fluid pressure to ensure it is within the specified range. Low pressure may indicate a problem with one or more solenoids.
- Replacement: If a faulty solenoid is identified, it should be replaced with a new one. Ensure the replacement solenoid is compatible with the specific transmission model.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the function of the solenoids in the ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 transmissions?
The solenoids control the flow of transmission fluid to different hydraulic circuits within the transmission, managing gear shifts and ensuring smooth operation.
2. How can I access the solenoid diagram for the ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 generation 2 transmissions?
The solenoid diagram can usually be found in the service manual for the specific vehicle model or obtained from the transmission manufacturer. It is also available in PDF format from various online sources.
3. What are common symptoms of solenoid failure in these transmissions?
Symptoms of solenoid failure include erratic shifting, transmission slipping, failure to engage certain gears, and diagnostic trouble codes related to the solenoids.
4. Can I replace a faulty solenoid myself, or do I need a professional?
While it is possible to replace a solenoid yourself if you have the necessary skills and tools, it is generally recommended to seek the assistance of a professional technician to ensure the repair is done correctly.
5. How often should the solenoids in the ZF 6HP19 and ZF 6HP21 transmissions be inspected or replaced?
The solenoids should be inspected during regular transmission maintenance intervals, typically every 30,000 to 60,000 miles. Replacement may be necessary if any issues are detected during inspection.
Conclusion
The ZF 6hp19 ZF6hp21 Generation 2 Solenoid Diagram PDF is an invaluable tool for anyone involved in the maintenance or repair of these advanced automatic transmissions. By understanding the layout and function of each solenoid, technicians can diagnose and resolve issues more efficiently, ensuring the continued performance and reliability of these transmissions. Regular inspection and maintenance of the solenoid pack are essential to prevent common problems and extend the lifespan of the transmission. Whether you are a professional mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, having access to the solenoid diagram and following proper diagnostic and repair procedures will help you keep your vehicle’s transmission in optimal condition.